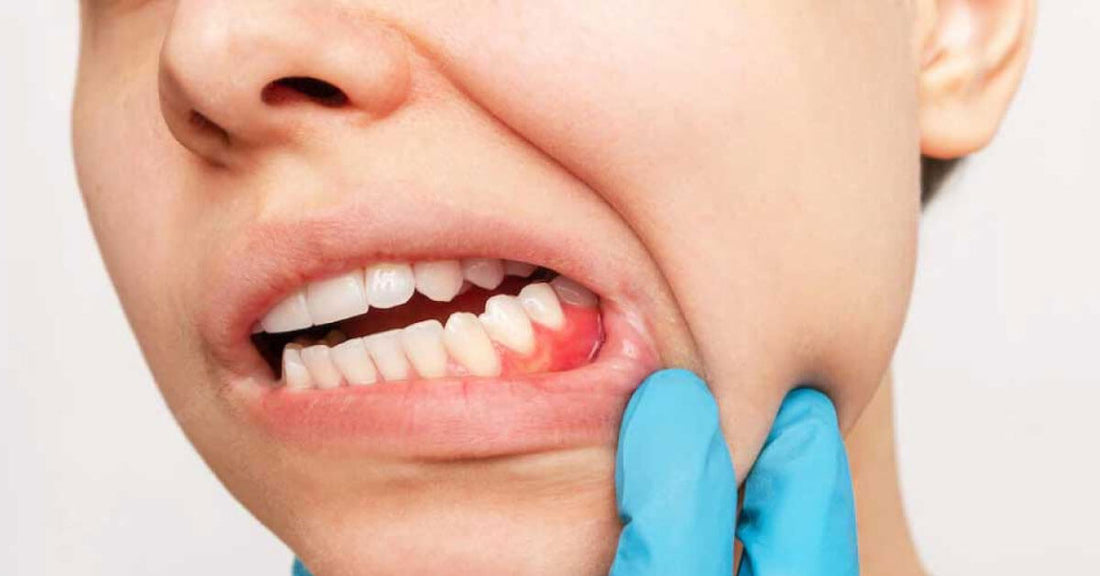
How to prevent and treat gum inflammation
Gum inflammation (also known as gingivitis, sometimes gingivitis) is a gum disease caused by plaque.
Bleeding gums are the first sign of infection. If untreated, it can progress to periodontitis and subsequent tooth loss. It is not advisable to underestimate gingivitis.
What is gum inflammation
The human body creates infection in places where dental plaque bacteria settle and accumulate. Gum inflammation is therefore a reaction to an excessive amount of bacteria irritating the gum surface.

What you need to know about gum inflammation:
- It is a common disease
- Gum inflammation is treatable if intervened early
- Long-term untreated inflammation can lead to tooth loss
- Gum inflammation is not contagious
How common is gum inflammation
Inflamed gums are a relatively common infection in the sequence of gum diseases. Inflammation is the precursor to much more serious disease - periodontitis.
What gum disease looks like:
- Healthy gums
- Acute gum inflammation
- Chronic gum inflammation
- Periodontal disease (periodontitis)
- Tooth loss
How long does gum inflammation last?
Gum inflammation has two levels of intensity. The early stage is acute gum inflammation, which occurs due to insufficient cleaning of teeth (usually mainly underestimating the cleaning between teeth). Acute inflammation subsides in about 3 weeks with careful cleaning using dental floss or an interdental brush.
When chronic gum inflammation breaks out, the gums start to recede (the gingival crevice deepens), and more intense bleeding occurs. Receding gums can continue to recede for years before they finally develop into periodontitis.
Is gum inflammation treatable?
In relation to the duration, it should be mentioned that gum inflammation is treatable in its early stages (i.e., acute gum inflammation). In the case of chronic inflammation, receding gums cannot be treated, but the problems with the gums can only be alleviated and the progression of the disease slowed down.
Is gum inflammation contagious?
No, it is not contagious, but it should not be underestimated. Mainly because it is only a stage of the disease leading to the loss of teeth. The moment when gum inflammation is painful should be an alarm for a visit to the doctor. This could indicate the onset of periodontal disease.
Causes of gum inflammation
Gum bleeding has many causes. The most common reason, as with sensitive teeth, is insufficient oral hygiene. Bleeding gums can also be caused by diseases, an unhealthy lifestyle, and even certain medications.
What causes gum inflammation:
- Poor hygiene (accumulated plaque and tartar)
- Lack of vitamins and minerals
- Smoking
- Stress and hormonal changes (pregnancy, puberty)
- Diabetes or the use of corticosteroids
- Certain viral and bacterial diseases (HIV, Herpes, Syphilis)
How oral hygiene affects gum inflammation
Insufficient hygiene and care for teeth lead to the accumulation of tartar, which subsequently creates a breeding ground for plaque that harms the gums. In the fight against gum inflammation, interdental cleaning is especially important, as bacteria survive most easily in the spaces between teeth.
The impact of vitamin and mineral deficiency on gum health
Without adequate nutritional intake in the form of vitamins and minerals, the mouth becomes a more hospitable environment for bacteria. A lack of vitamins weakens the body's fight against bacteria and dries out the mouth, thereby making it easier for bacteria to remain in the oral cavity. A mineral deficiency weakens the teeth, contributes to the development of canker sores, and thus facilitates the proliferation of bacteria.

The most useful vitamins for healthy gums are vitamins A, C, and D. You can never go wrong with vitamin C because it helps keep the entire immune system strong. The immune system, in turn, fights gum diseases more effectively. Vitamin A protects against dry mouth, and vitamin D helps in the fight against gum inflammation according to recent studies.
Among the minerals that contribute most to a healthy oral cavity are iron and calcium. A lack of iron contributes to the development of inflammation on the tongue, which subsequently causes canker sores in the mouth. Calcium helps maintain strong tooth enamel and prevents cavities. Both minerals create a more challenging environment for bacteria to survive in the mouth.
Influences of lifestyle on gums
Smokers are twice as likely to develop gum inflammation as non-smokers. Unfortunately, this article will sound repetitive. Smoking harms health, including the health of the gums. The gums of smokers suffer mainly due to a smoking-weakened overall immune system. This causes lower resistance to inflammation and slower gum healing.
Gum inflammation due to hormonal changes in pregnancy, manifesting as more intense gum bleeding, affects a large number of pregnant women. During the hormonal roller coaster of pregnancy, it is therefore important, among other things, to carefully monitor gum health. Women with healthy gums before pregnancy have a great chance of avoiding pregnancy gingivitis.
Gum inflammation can also occur in children during puberty. The cause is hormonal changes, just as in pregnant women. Children often exacerbate the inflammation with insufficient oral hygiene.
No less significant hormonal change is continuous stress creating a higher level of cortisol in the blood. According to some studies, excessive production of cortisol in the body correlates with gum disease, especially due to the negative effects of cortisol on the immune system. It cannot be said with certainty that there is a causal relationship between stress and gum inflammation, but it can be argued that stress to some extent can contribute to the development of gum disease.
Influences of diseases on gums
Bleeding teeth during cleaning, unfortunately, are not uncommon when treating some serious diseases. People with diabetes and those suffering from serious viral (HIV, Herpes) or bacterial (Syphilis, Gonorrhea) diseases mainly experience gum problems.
People with diabetes have a higher level of glucose (sugar) in their blood, respectively in their saliva and gums. The bacteria in dental plaque on the gum surface feed on sugars. This environment suits them, and they can multiply and accumulate more easily. This subsequently increases the chance of inflammation.
Viral and bacterial diseases are generally very invasive to the human immune system. Therefore, the health of the oral cavity is also affected. The most serious cause is HIV, which inherently causes a disorder of the body's anti-infection function. In this disease, the gums bleed and hurt.
In some cases, the treatment itself can weaken the immune system as a whole. For example, treatment with corticosteroids is relatively common. Corticosteroids are primarily used to suppress the immune system, respectively to block autoimmune or strongly allergic reactions. For this reason, corticosteroids are feared by some dentists in relation to gum health.
Symptoms of gum inflammation
How to recognize gum inflammation? Relatively easily. The first symptom is painless bleeding of the gums when brushing teeth. In the subsequent stage, the gums recede, bleed, and hurt.
What are the symptoms of gum disease:
- Painless bleeding of the gums when brushing teeth
- Swollen, irritated gums
- Receding gums, exposed tooth roots
- Painful bleeding of the gums in the most severe stage
What gum inflammation looks like
Bleeding from the gums is the first sign of inflammation. Initially, it occurs especially when cleaning between the teeth. As the infection breaks out, bleeding becomes more common even with normal cleaning. The gums will be irritated to swollen.
Gum inflammation and pain
If you are experiencing painful gum inflammation, you might be wondering, “Will I lose my teeth?”. Gum inflammation usually does not hurt. Painful gums are rather a symptom of the subsequent periodontitis. That causes tooth loss. However, the process of loss is not immediate. Visit a dentist, and they will prepare a system for treating gum inflammation.
Prevention of gum inflammation
It needs to be repeated several times that gum inflammation is caused in most cases by insufficient teeth cleaning. Conscientious dental care is the best way to stop receding gums and inflammation. You may completely avoid gum inflammation. If you do get inflammation, it can be treated with more suitable dental care products or over-the-counter medications.
5 principles of teeth cleaning:
- Brush your teeth for 2 minutes twice a day
- Use a brush with soft bristles
- Choose toothpaste with antibacterial and remineralization effects
- Don't forget to clean between your teeth and your tongue
- After brushing your teeth, rinse your mouth with mouthwash
Treatment of gum inflammation
Let's say you failed to prevent an infection from occurring. At such a moment, dental care becomes even more important. There is no need to intensify teeth cleaning; twice a day is sufficient. However, it is wise to consider changing dental care products for a more effective fight against gum inflammation.
What to use for gum inflammation:
- Use toothpaste containing chlorhexidine (max 1-2 weeks)
- Rinse mouth with an antibacterial mouthwash
- Use only a soft or extra-soft toothbrush
- Clean the spaces between your teeth every day
- Clean your tongue more carefully
Gum inflammation: what helps to diagnose it?
A gum bleeding test using a special dental probe can be performed if gum inflammation is suspected. The dentist measures the condition of the gums (applying the probe for about 20 seconds at several points on the gums) and evaluates the PBI (Papilla Bleeding Index) ranging from 0 to 4.
How to interpret the PBI Index:
- PBI 0 = Healthy gums (no bleeding)
- PBI 1 = Bleeding only at certain points of the gum (spot bleeding)
- PBI 2 = Bleeding along a longer section of the gum (line bleeding)
- PBI 3 = Blood flows to the area around the neck of the tooth (filling of the interdental spaces)
- PBI 4 = Gums bleed very much and are very sensitive (spontaneous bleeding)
What helps with gum bleeding?
It's relatively easy to get rid of gum bleeding in the early stages of the disease. Cleaning the spaces between your teeth daily and paying more attention to dental hygiene should heal bleeding gums within 1-3 weeks. Special antibacterial toothpastes and mouthwashes can help accelerate the treatment of gum inflammation.
Acute gum inflammation treatment requires time. There is no absolute solution to immediately stop gum recession when cleaning.
Can gum inflammation be reversed?
Hygiene is the way to cure gum inflammation in the acute early stage. Once the condition moves into chronic gum inflammation, regular cleaning may not be a sufficient solution to cure gingivitis.
In general, gum inflammation in the form of gingivitis is treatable. It becomes untreatable when it is long-neglected and develops into periodontitis. At that stage, painful gum inflammation can also occur.
What about gum inflammation
Dentists usually can't do more than recommend a consultation with a dental hygienist and her professional cleaning of plaque and tartar. Subsequently, visit a dental hygienist at least twice a year for professional cleaning. The treatment with regular and careful oral hygiene is entirely in your hands.
Natural treatment for gum inflammation
What herbs to use in a treatment course for bleeding gums? Rinses made from sage, oak bark, chamomile, and marshmallow are generally recommended. Whether natural treatment is a proven way to get rid of gum inflammation is debatable, but it certainly won't harm you.
What to use for bleeding gums (herbs):
- Sage
- Oak bark
- Chamomile
Over-the-Counter treatment for bleeding gums
Over-the-counter treatment for gingivitis covers most cases of gum inflammation. Antibiotics, which are not available over the counter, are used only in the most severe cases.
Medications for bleeding gums are primarily dental care products containing chlorhexidine. Medicinal products for throat inflammation (gargles), although not primarily intended as medications for bleeding gums, can also be helpful.
Prescription medications for gum inflammation
In exceptional cases accompanied by fever and a strong to painful inflammatory reaction, a dentist may prescribe antibiotics for gum inflammation, and possibly analgesics as well.
Dental care products for gum inflammation
What is good for gum inflammation? Based on our tests, we have selected the best products for you (some of which you can find in our online store).
Interdental cleaning is most important
Cleaning the spaces between your teeth is the most important part of treating gingivitis. Suitable products for cleaning hard-to-reach places between the teeth include interdental brushes with soft bristles or dental floss.
The best toothpastes for gum inflammation
For preventive purposes, almost any quality toothpaste is sufficient. But what is the best toothpaste for receding gums or gingivitis? Ideally, choose one with a higher concentration of antibacterial ingredients. The most recommended treatment includes products containing zinc or chlorhexidine. Be cautious with chlorhexidine, as it cannot be used daily (max 1-2 weeks until acute gum inflammation subsides).
Keep in mind that even toothpaste with chlorhexidine does not replace interdental cleaning. An interdental brush or dental floss remains the key element in fighting gum inflammation.
Antibacterial mouthwash helps fight inflammation
Rinsing with mouthwash after brushing helps remove bacteria that settle in the oral cavity. Additionally, the water can easily penetrate hard-to-reach places between the teeth.
For treatment, choose a mouthwash containing chlorhexidine. For prevention, opt for mouthwashes with antibacterial ingredients such as natural substances Caprylic/Capric Triglyceride or Tea Tree Oil.
The brush must have soft bristles
The brush does not play a crucial role in the fight against gum inflammation (cleaning technique is more important). It is essential to ensure that the brush does not harm you with its bristles. Therefore, choose soft or extra soft toothbrushes.
Tongue cleaning is often overlooked
Last but not least, tongue cleaning should be mentioned. There are studies confirming the positive impact of tongue cleaning on both breath odor and gum inflammation. You can use special products or a regular toothbrush.
---
Always discuss any gum issues with your dentist.
---